Join our Facebook Group
Peak-end rule
The Peak-End Effect is a cognitive bias that causes people to remember an experience by the Peak (the most intense positive or negative point) and the end (the final moments) rather than the totality of the event itself.
Essentially, the Peak-End effect means that people will only remember the experience on your website by the most intense point and the end of the experience. For example, if your website offers great products (Peak) but the checkout experience is poor (End), there is a good chance that it might overwhelm the chances of your customer remembering the experience as great. This might cause potential and current customers to become one time buyers which will be bad for your business.
Peak-End Theory
To get a better understanding of the peak-end rule bias we've got to dive into how it works. Specific memories are important to how we look back on an experience. That's the result of how our brains work. This is something Kahneman explains in his book 'Thinking Fast and Slow'. Not up for reading? Down below is a video.
Summary: We make decisions through two systems. System 1 is being responsible for quick decisions (should I flee or attack?) and barely takes any energy. System 2 we use for complex decisions (do I want to spend $1100 on a new smartphone while my current one is still working?).
Peak-end Rule Real Life Example
Have you ever been to the IKEA? If yes, you know that you can buy this hotdog at the end for a sweet price. This is something you can do after check-out. There are two situations
- You've found what you're looking for, but having to pay for it is never fun.
- You couldn't find what you were looking for, in that case, you're disappointed.
Both situations are a little bit painful for our brains. IKEA realized this and figured they had to do something about this. How you remember a particular activity is more important than how you experienced the activity as a whole. That's when they came up with the idea to sell the hotdogs for a relatively low price after you are done shopping.
In short, a lot of people buy this hotdog after they have been shopping. This is their peak-end experience and not the two situations I outlined earlier. In general, the customers are now happier when they leave IKEA. IKEA choose to do something with food. Food gives positive signals to the brain.
How Can One Use the Peak-End Effect?
The first step you should take is to identify what the peak moments are, when and why they occur. Carefully go through your customers' journey and identify the emotional highs and lows customer experience as they interact with your digital property. When you can identify what peaks currently exist in your customers' journey, then you can work on making the peak experiences positive.
You don't necessarily have to do anything expensive or elaborate to delight customers, you can easily create positive peak experiences with simple actions like using their names, remembering important dates or simplifying a process.
End The Experience With A Bang! Find out what you can implement to ensure customers end their interaction with your business on a very high note. Make it a grand finale to ensure customers remember and feel positive emotions at the end of their interaction with your business. This can be achieved in several ways like a; sincere goodbye, surprise discount at checkout or by even providing a small departure gift as the customers' exit.
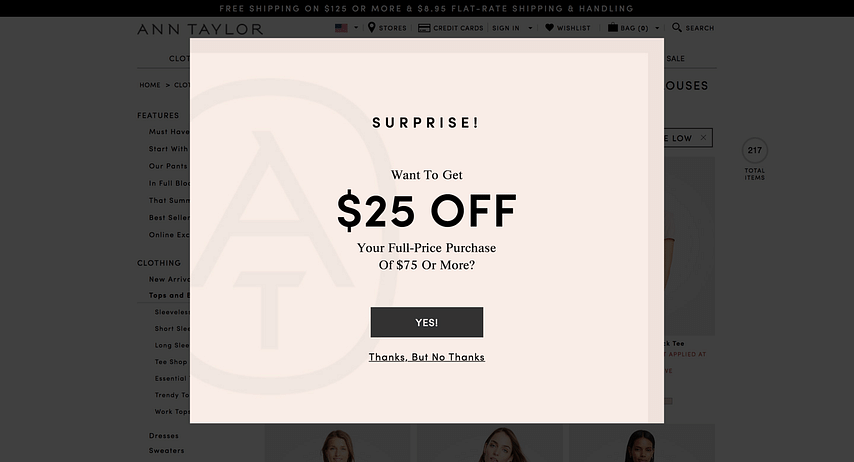
The Ann Taylor website displays a popup that offers a surprise discount when a user tries to exit the site or open another browser tab.
Peak-End Bias After Check-Out
Usually, confirmation pages are not seen as an important part of the funnel and can sometimes be neglected because the purchase has already been made, but it's still optimization and can help to encourage repeat business, positive recommendations, or fewer early cancellations.
In the Netherlands, there is an app called Tikkie. It's an app that can be used to send somebody a payment link (it's much more, but that's the basic idea). Paying is never fun and that's something they realized. After you've paid somebody with the app they will show you a fun GIF. You will close the app with a smile (most of the time).
References
The references contain experiments and studies that prove this bias is there.
Books
Would you like to go more in-depth? Here are our recommendations:


Will you use psychology for your experimentation process?
Are you curious about how to apply this bias in experimentation? We've got that information available for you!
Join over 452+ users
- Lifetime access to all biases
- Filter on metrics, page type, implementation effort
- More examples and code for experimentation
Choose your subscription!
Pay with Stripe
Lifetime deal PREMIUM
Get access to the search engine, filter page, and future features.