Join our Facebook Group
Attentional bias
Attentional bias refers to how a person's perception is affected by selective factors in their attention. Attentional biases may explain an individual's failure to consider alternative possibilities when occupied with an existing train of thought. For example, cigarette smokers have been shown to possess an attentional bias for smoking-related cues around them, due to their brain's altered reward sensitivity.
What Is The Attentional Bias All About?
Essentially, attentional bias involves the tendency to pay attention to some things while simultaneously ignoring others. This impacts not only the things that we perceive in the environment but the decisions that we make based upon our perceptions. When you are trying to make an important decision, do you always consider all of the possibilities? While we might like to think that we take all the alternatives into consideration, the reality is that we often overlook some options and possible outcomes. In some cases, our attention becomes focused on just a few of the options while we ignore the rest.
If you have ever been in a frightening situation and experienced what is often referred to as "tunnel vision" in which you become hyper-aware and acutely focused on a specific threat, you can probably see how this tendency can be helpful.
How Can One Manage Attentional Bias?
In using Attentional Bias to aid users in making mutually beneficial decisions, one would have to recognize that the first point of contact is visual. Website visitors respond heavily to visual stimulants and have a finite capacity for attention. As much as we try to convince ourselves otherwise, people can really only focus on a small number of things at a time and that is why one should take advantage of this information and use it to improve upon their design to offer the best possible experience a user can get.
Familiarity can go a long way as well: the more often a person sees your name, logo, or call to action, the more likely they are to purchase from you. Place calls to action throughout your landing pages, pay to retarget your visitors with ads: repeated exposure to your message makes a customer more likely to buy
Attentional Bias example
Example: Ever noticed how Amazon sometimes reminds you about items on your wishlist or even stuff that you just casually browsed? That's an obvious use of attentional bias right there.
Be aware of how this might impact your decisions as an experimenter. The more often you see a certain test in case of studies, for example, the more likely you are to blindly believe that test will be applicable to your site.
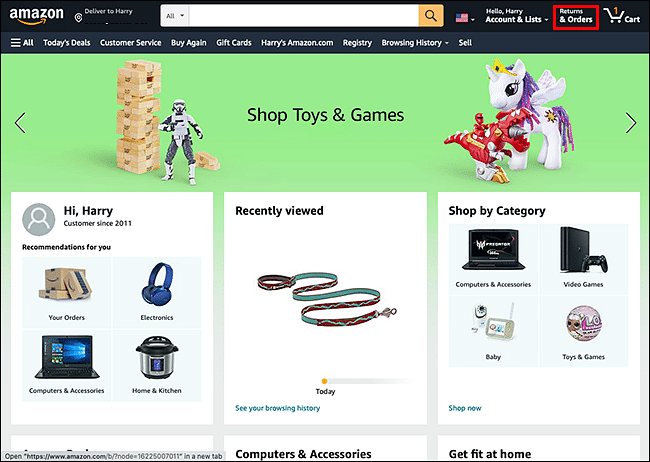
Example of hypothesis applied
If we showcase recently bought products, then conversions for signed up users on all devices will increase, because of Attention bias.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will you use psychology for your experimentation process?
Are you curious about how to apply this bias in experimentation? We've got that information available for you!
Join over 452+ users
- Lifetime access to all biases
- Filter on metrics, page type, implementation effort
- More examples and code for experimentation
Choose your subscription!
Pay with Stripe
Lifetime deal PREMIUM
Get access to the search engine, filter page, and future features.